- Load the R packages we will use.
Download \(CO_2\) emissions per capita from Out World in Data into the directory for this post.
Assign the location of the file to
file_csv. The data should be in the same directory as this file.
- Read the data into R and assign it to
emissions
file_csv <- here("_posts",
"2021-02-23-reading-and-writing-data",
"co-emissions-per-capita.csv")
emissions <- read_csv(file_csv)
- Show the first 10 rows (observations of)
emissions
emissions
# A tibble: 22,383 x 4
Entity Code Year `Per capita CO2 emissions`
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Aruba ABW 1950 10.8
2 Aruba ABW 1951 17.0
3 Aruba ABW 1952 9.56
4 Aruba ABW 1953 10.8
5 Aruba ABW 1954 20.8
6 Aruba ABW 1955 16.4
7 Aruba ABW 1956 20.3
8 Aruba ABW 1957 13.3
9 Aruba ABW 1958 11.0
10 Aruba ABW 1959 13.6
# ... with 22,373 more rows- Start with
emissionsdata THEN
- use
clean_namesfrom the janitor package to make names easier to work with - assign the output to
tidy_emissions - show the first 10 rows of
tidy_emissions
tidy_emissions <- emissions %>%
clean_names()
tidy_emissions
# A tibble: 22,383 x 4
entity code year per_capita_co2_emissions
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Aruba ABW 1950 10.8
2 Aruba ABW 1951 17.0
3 Aruba ABW 1952 9.56
4 Aruba ABW 1953 10.8
5 Aruba ABW 1954 20.8
6 Aruba ABW 1955 16.4
7 Aruba ABW 1956 20.3
8 Aruba ABW 1957 13.3
9 Aruba ABW 1958 11.0
10 Aruba ABW 1959 13.6
# ... with 22,373 more rows- Start with the
tidy_emissionsTHEN
- use
filterto extract rows withyear == 2000THEN - use
skimto calculate the descriptive statistics.
| Name | Piped data |
| Number of rows | 219 |
| Number of columns | 4 |
| _______________________ | |
| Column type frequency: | |
| character | 2 |
| numeric | 2 |
| ________________________ | |
| Group variables | None |
Variable type: character
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | min | max | empty | n_unique | whitespace |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entity | 0 | 1.00 | 4 | 32 | 0 | 219 | 0 |
| code | 12 | 0.95 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 207 | 0 |
Variable type: numeric
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | mean | sd | p0 | p25 | p50 | p75 | p100 | hist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| year | 0 | 1 | 2000.00 | 0.00 | 2e+03 | 2000.00 | 2000.00 | 2000.00 | 2000.00 | ▁▁▇▁▁ |
| per_capita_co2_emissions | 0 | 1 | 5.06 | 6.74 | 2e-02 | 0.71 | 2.82 | 7.97 | 58.39 | ▇▁▁▁▁ |
- 13 observations have a missing code. How are these observations different?
- start with
tidy_emissionsthen extract rows withyear == 2000and are missing a code.
# A tibble: 12 x 4
entity code year per_capita_co2_emissions
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Africa <NA> 2000 1.11
2 Asia <NA> 2000 2.40
3 Asia (excl. China & India) <NA> 2000 3.35
4 EU-27 <NA> 2000 8.46
5 EU-28 <NA> 2000 8.61
6 Europe <NA> 2000 8.48
7 Europe (excl. EU-27) <NA> 2000 8.47
8 Europe (excl. EU-28) <NA> 2000 8.19
9 North America <NA> 2000 14.6
10 North America (excl. USA) <NA> 2000 5.39
11 Oceania <NA> 2000 12.6
12 South America <NA> 2000 2.32Entities that are not countries do not have country codes.
- Start with
tidy_emissionsTHEN
- use
filterto extract rows with year == 2000 and without missing code THEN - use
selectto drop theyearvariable THEN - use
renameto change the variableentitytocountry - assign the output to
emissions_2000
- Which 15 countries have the highest
per_capita_co2_emissions?
- start with
emissions_2000THEN - use
slice_maxto extract the 15 rows with theper_capita_co2_emissions - assign the output to
max_15_emitters
max_15_emitters <- emissions_2000 %>%
slice_max(per_capita_co2_emissions, n = 15)
- Which countries have the lowest
per_capita_co2_emissions?
- start with
emissions_2000THEN - use
slice_minto extract the 15 rows with the lowest values - assign the output to
min_15_emitters
min_15_emitters <- emissions_2000 %>%
slice_min(per_capita_co2_emissions, n = 15)
- Use
bind_rowsto bind together themax_15_emittersandmin_15_emitters
- assign the output to
max_min_15
max_min_15 <- bind_rows(max_15_emitters, min_15_emitters)
- Export this
max_min_15to 3 file formats.
max_min_15 %>% write_csv("max_min_15.csv") # comma-separated values
max_min_15 %>% write_tsv("max_min_15.tsv") # tab separated
max_min_15 %>% write_delim("max_min_15.psv", delim = "|") # pipe-separated
- Read the 3 file formats into R
max_min_15_csv <- read_csv("max_min_15.csv") # comma-separated values
max_min_15_tsv <- read_tsv("max_min_15.tsv") # tab separated
max_min_15_psv <- read_delim("max_min_15.psv", delim = "|") # pipe-separated
- Use
setdiffto check for any differences amongmax_min_15_csv,max_min_15_tsvandmax_min_15_psv
setdiff(max_min_15_csv, max_min_15_tsv, max_min_15_psv)
# A tibble: 0 x 3
# ... with 3 variables: country <chr>, code <chr>,
# per_capita_co2_emissions <dbl>Are there any differences?
- Reorder
countryinmax_min_15for plotting and assign to max_min_15_plot_data
- start with
emissions_2000THEN - use
mutateto reordercountryaccording toper_capita_co2_emissions
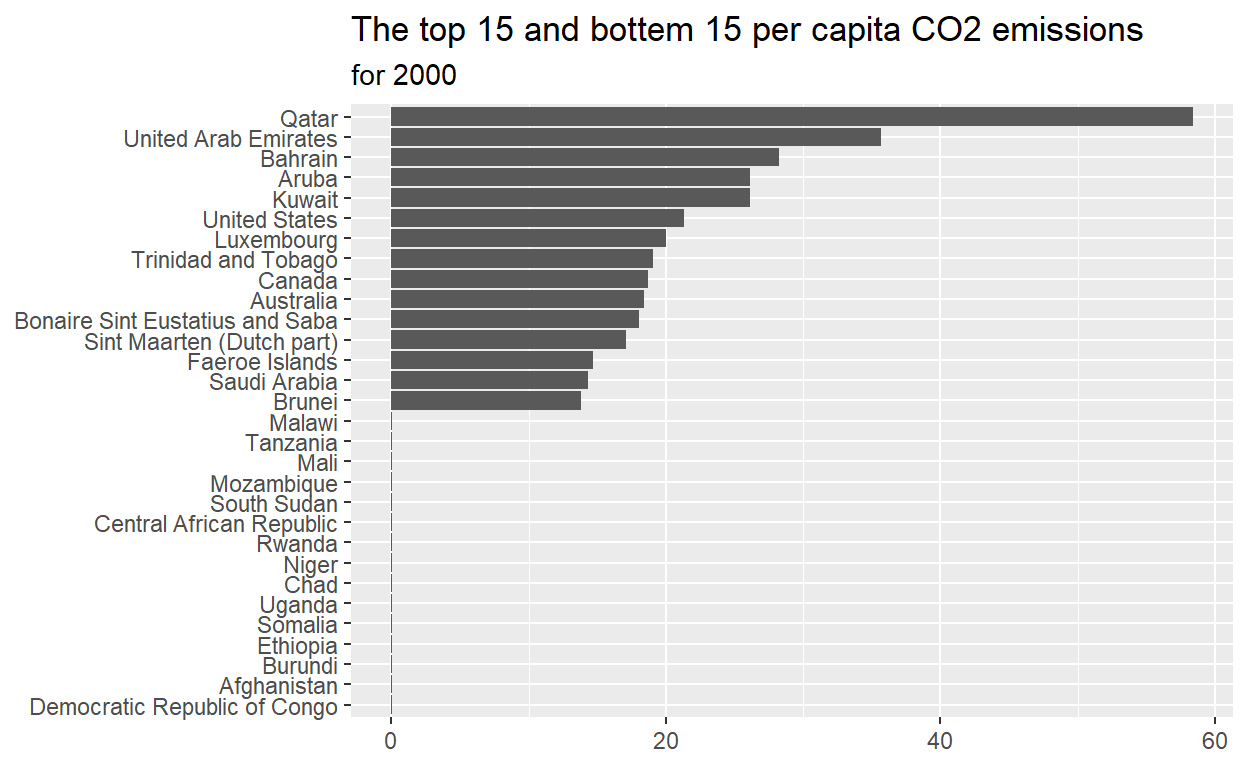
max_min_15_plot_data <- max_min_15 %>%
mutate(country = reorder(country, per_capita_co2_emissions))
- Plot
max_min_15_plot_data
ggplot(data = max_min_15_plot_data,
mapping = aes(x = per_capita_co2_emissions, y = country)) +
geom_col() +
labs(title = "The top 15 and bottem 15 per capita CO2 emissions",
subtitle = "for 2000",
x = NULL,
y = NULL)
- Save the plot directory with this post.
ggsave(filename = "preview.png",
path = here("_posts", "2021-02-23-reading-and-writing-data"))
- Add preview.png to yaml chuck at the top of this file.
preview: preview.png